
The growing global burden of cardiovascular, cardiorenal, and cardiometabolic diseases calls for urgent action in primary care.
Most cardiovascular diseases are preventable by addressing modifiable risk factors, such as:
The effects of these risk factors often present as raised blood pressure, elevated blood glucose, high blood lipids, and obesity—key indicators of increased risk for heart attack, stroke, heart failure, and other complications. These intermediate risk factors can be identified and managed in primary care settings, where an estimated 90% of patients are diagnosed and treated.
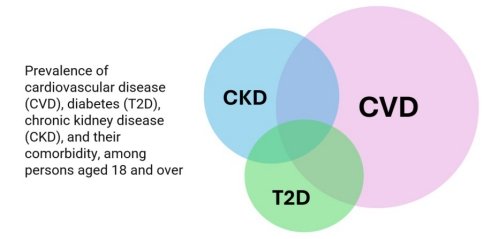
T2D & CKD significantly increase CVD risk and contribute to the progression of:
The co-existence of CVD, CKD, and T2D not only increases the risk of adverse outcomes but also leads to higher overall and CVD-related mortality.
Obesity is a major, yet often overlooked, driver of cardiovascular disease. It contributes to hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, and inflammation, all of which accelerate the development of CVD. Managing weight through lifestyle interventions, medications, and, where appropriate, bariatric procedures can significantly reduce cardiovascular risk and improve long-term health outcomes.
Despite the availability of international guidelines, their implementation in primary care remains delayed. As discussed in a recent EPCCS Council meeting, ensuring that primary care professionals have access to practical, applicable guidance is crucial for improving patient outcomes.
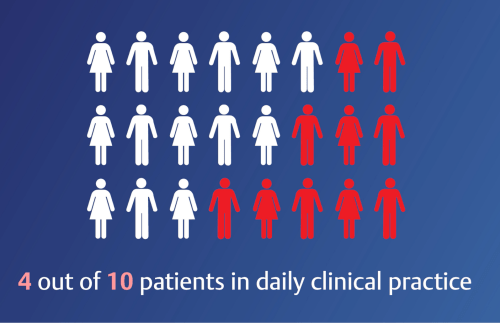
Primary care professionals play a pivotal role in combating CVD, CKD, and T2D. Ensuring early detection, lifestyle interventions, and appropriate medical treatment can prevent premature deaths and reduce the global burden of cardiovascular disease.
By taking proactive steps, primary care can drive change, save lives, and improve cardiovascular health worldwide